Laser-cutting technology plays an increasingly important role in modern manufacturing. This technology is widely used in many fields, from automobile manufacturing to aerospace, and even artistic creation and medical equipment, due to its high precision, high efficiency, and flexibility. This article will introduce the basic process of laser cutting, the main type,s and its wide range of applications in detail.
What is laser cutting?
Laser cutting is a high-precision material processing technology that cuts on the surface of the material by focusing the high energy of the laser beam. The laser beam is collimated and focused by the optical system to form an extremely small and intense spot, which can quickly heat the material to a molten or vaporized state. Using this concentrated energy, the laser cutting machine can make precise cuts on a variety of materials, including metal, plastic, wood, glass, etc.
Compared with traditional cutting methods, laser cutting can not only achieve higher cutting accuracy and smoother cutting edge but also can handle complex shapes and subtle details. It is widely used in manufacturing, architectural decoration, artistic creation, and other fields.

How Laser Cutting Machines Work
1 . Generation of G-code
Before the laser cutting process can take place, the first step is to generate the code. This code is a language that the machine can understand. It provides instructions on how and where the cutting head should move and represents the pattern that must be cut into the material. G-code is written using CAM software and transmitted via a cable or internet connection.
2.Generation and amplification of the laser beam
Next is the generation of the laser beam. This process takes place inside the laser cutting machine using a gain medium, optical elements, and two mirrors. Note that the two mirrors are not alike; one is reflecting, while the other partially reflects the light. When energy is supplied to the gain medium, the electrons present are excited to a higher energy level. When it relaxes to a metastable state, it releases a photon.
This photon interacts with another electron, releasing another photon of the same wavelength. This cascade reaction results in the amplification of the light. When the gain medium is located between the two mirrors. The amplified photons pass through the slightly transparent mirrors to form a laser beam.
3.Cutting process
The cutting process involves directing the laser beam to the area to be cut. This process uses a lens that focuses the beam into a small diameter. When the laser beam comes into contact with the material surface, it melts and cuts the material. At the same time, an inert gas (such as argon or nitrogen) blows the molten material away, leaving a fine cut.
Note: Before metal forming, make sure you set the laser parameters, including laser power, focal length, and speed.
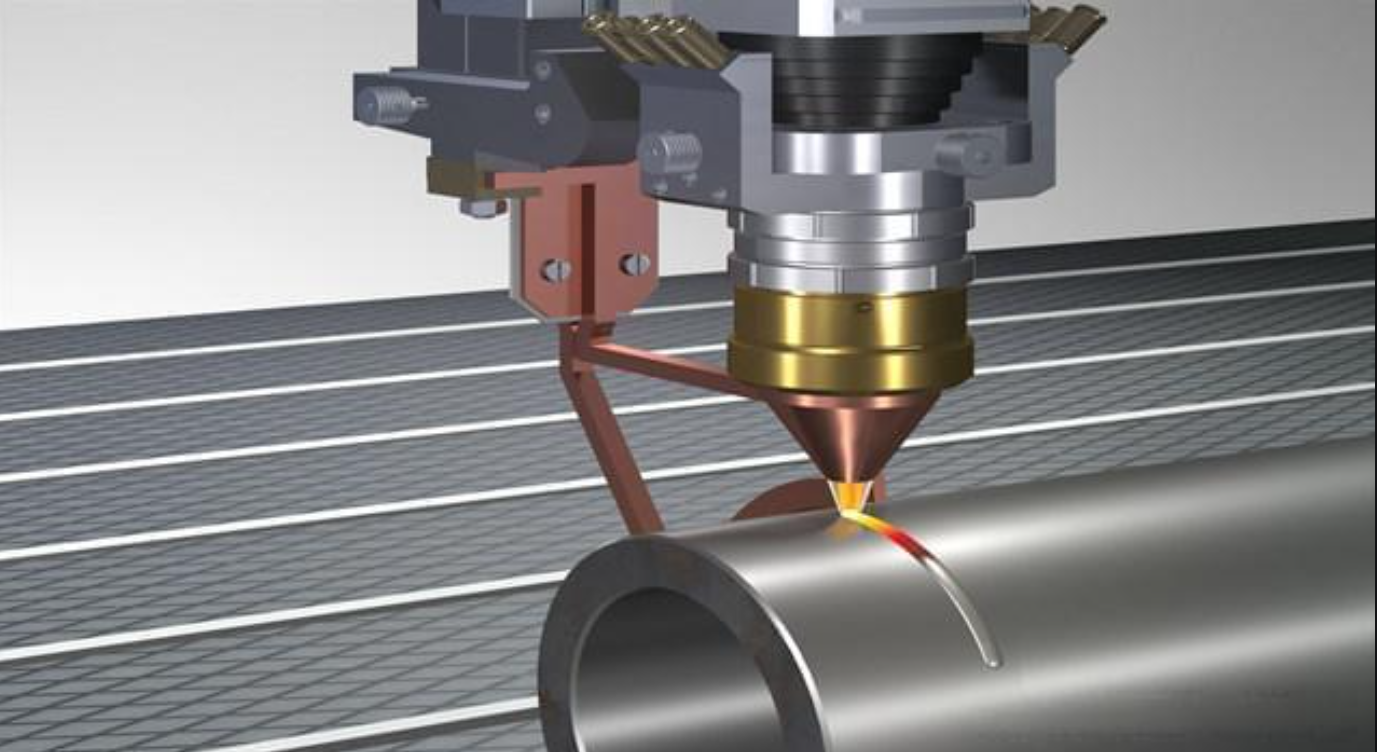
4.Cooling and finishing
Many laser-cutting machines have built-in cooling systems to prevent overheating. Once you have the final product, you can use other post-processing techniques to improve the surface finish.
Main types of laser cutting
1.CO2 laser cutting
CO2 laser cutting uses a carbon dioxide laser as a light source. The wavelength of light emitted by a CO2 laser is about 10.6 microns, which is suitable for cutting metals, non-metals, and composite materials. The advantages of CO2 laser cutting include:
- Wide material adaptability: Able to cut a variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, plastics, wood, etc.
- Good cutting quality: Able to achieve high-quality cutting edges and details.
2. Fiber laser cutting
Fiber laser cutting uses a fiber laser as a light source. The wavelength of light from a fiber laser is about 1.06 microns. The advantages of fiber laser cutting include:
- High energy efficiency: The energy conversion efficiency of fiber lasers is higher than that of CO2 lasers, which can save energy consumption.
- High cutting speed: Fiber laser cutting is faster and suitable for mass production.
- Low maintenance cost: Fiber lasers have low maintenance costs and long service life.
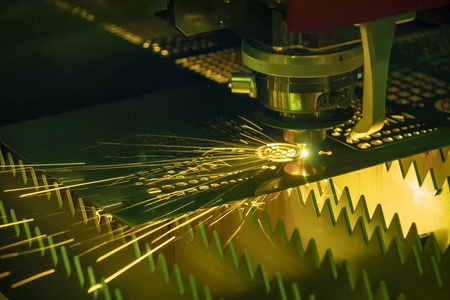
3.YAG laser cutting
YAG laser cutting uses yttrium aluminum garnet laser (YAG) as the light source. The wavelength of YAG laser light is about 1.064 microns. The characteristics of YAG laser cutting include:
- High power output: suitable for cutting thicker metal materials.
- Good beam quality: capable of high-precision cutting.
Application of laser cutting
1. Manufacturing industry
- Automobile manufacturing: Laser cutting is used to make automobile body panels, frames, interior components, etc., and can achieve high-precision cutting and complex shapes.
- Aerospace: Used to manufacture high-strength material components such as lightweight alloys and aviation parts to meet high precision and high-performance requirements.
- Electronic equipment: Used to cut circuit boards, electronic components, and other electronic components to ensure the accuracy and functionality of circuits.
2. Medical equipment
- Surgical instruments: Laser cutting can make high-precision scalpels, tweezers, etc. to ensure fine operation and safety during surgery.
- Medical implants: Used to cut and process biomaterials and manufacture various medical implants such as artificial joints, dental restorations, etc.
3. Art and creativity
- Sculpture and installation art: Laser cutting can make complex sculptures and art installations to help artists achieve innovative designs.
- Personalization: Used to make customized gifts, souvenirs, decorations, etc. to meet the needs of personalization and uniqueness.
Advantages of laser cutting
1. High-precision and high-quality cutting
A significant advantage of laser cutting is its excellent precision and cutting quality. The laser beam can be focused on a very small spot, generating highly concentrated heat, which enables laser cutting to achieve extremely precise cutting, smooth edges, and almost no post-processing. Since there is no physical contact during the laser-cutting process, the heat-affected zone of the material is small, thus avoiding deformation and internal stress.
2. Flexibility and adaptability
Another major advantage of laser cutting technology is its high flexibility and adaptability. Laser-cutting machines can handle a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, glass, etc., and can cut materials of different thicknesses. The computer control system of the laser cutting machine makes it very convenient to design and adjust the cutting path, and complex shapes and customized designs can be easily achieved. This technology is not only suitable for mass production but also can flexibly respond to the needs of small-scale production and prototype manufacturing.

3. High efficiency and low cost
The high efficiency and low cost of laser cutting technology are another significant advantage. The processing speed of laser cutting machines is usually faster, which can significantly improve production efficiency. Due to the high accuracy of laser cutting, production costs are reduced by reducing material waste and the need for subsequent processing and trimming. There is no physical contact during the laser cutting process, which reduces tool wear and maintenance costs, and also makes the cutting process more stable and reliable.
Conclusion
Laser-cutting technology has become an indispensable processing method in modern manufacturing due to its high precision, high efficiency, and wide material adaptability. From industrial manufacturing to artistic creation, the application fields of laser cutting are constantly expanding. With the continuous advancement of technology, the performance and application scope of laser cutting will continue to improve, bringing more innovation and development opportunities to all walks of life.
