A waveguide is a structure used to guide electromagnetic waves in a direction. In electromagnetism and communication engineering, the term waveguide can refer to any linear structure that transmits electromagnetic waves between its endpoints, originally and most commonly used to mean a hollow metal tube used to transmit radio waves.
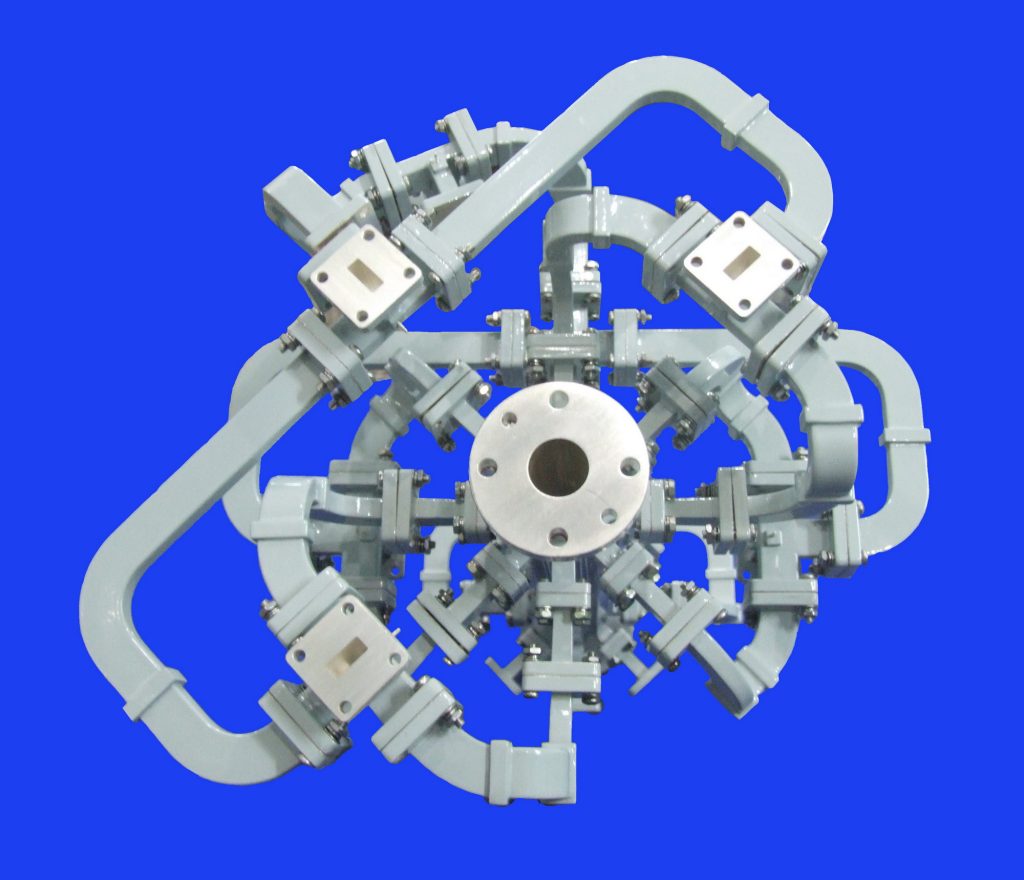
waveguide
Waveguides are primarily used as transmission lines at microwave frequencies, used in microwave ovens, radar, communication satellites, and microwave radio link equipment to connect microwave transmitters and receivers to their antennas.
Common structures mainly include parallel twin wires, coaxial lines, parallel slab waveguides, rectangular waveguides, circular waveguides, microstrip lines, slab dielectric optical waveguides, and optical fibers. From the perspective of guiding electromagnetic waves, they can be divided into inner and outer regions, and electromagnetic waves are limited to propagating in the inner region (requiring the transverse resonance principle to be satisfied within the waveguide cross-section).
NOTE: The most common form of waveguide is a metal tube. Other forms are (electric) dielectric rods or hybrid components consisting of conductive and dielectric materials.
It is a structure used to confine or guide electromagnetic waves. Generally, waveguides refer to hollow metal waveguides and surface waveguides of various shapes. The former completely confines the transmitted electromagnetic waves in the metal tube, also known as closed waveguides:
The latter confines the guided electromagnetic waves around the waveguide structure, also known as an open waveguide. As radio wave frequencies increase to the centimeter-wave and millimeter-wave bands of 3000 MHz to 300 GHz, the use of coaxial cables is limited to metal waveguides or other waveguiding devices.
