Solder projections are generally easy to appear on the solder feet of through-hole parts with long or thick feet, and other parts that are easier to dissipate heat (such as heat sinks or grounding pins) may also occur.
This is because the contact time between the part and the wave solder liquid is too short, and the temperature supply is insufficient, causing the tin liquid to cool down and solidify before the solder leg of the part leaves the tin pool before falling into the tin pool or rebounding solder joint.
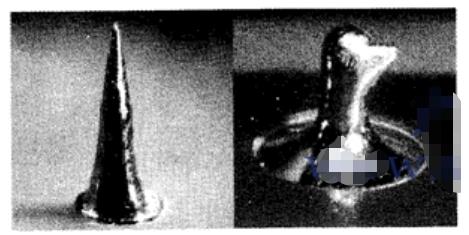
If the temperature loss is caused by long legs, it is recommended to change to short legs, but it should be noted that if it is cut into short legs before wave soldering in the factory, attention must be paid to the oxidation of the cut surface.
Suppose the temperature loss is caused by the connection of the part’s solder leg to a large-area metal sheet. In that case, it is recommended to increase the preheating temperature or slow down the chain speed so that the large-area metal sheet of the part can increase the temperature. Still, the heat resistance of other wave soldering parts should be considered question.
In fact, the main reason for solder projections in the wave soldering process is that the temperature of the solder fillet is too low. Thinking from another perspective, the temperature of the molten tin is too low, which makes the tin liquid too viscous. Imagine the situation of cheese wire drawing. When the temperature rises, the situation of cheese drawing will be improved.
The copper content in the tin pool exceeds the standard, causing the melting point of the tin pool to rise, and the flow of tin liquid becomes viscous
Therefore, in addition to the easy heat dissipation of the solder feet of the parts, the reason for the drop in the temperature of the tin liquid is that the composition of the tin pool is also a key point. When the copper content in the tin pool is higher, the melting point of the tin pool will be higher. If there is no increase, if the temperature of the tin pool is increased, the flow of the tin liquid will become viscous.
Unfortunately, most of the PCB or component pins contain copper metal, and lead-free solders using SAC (tin-silver-copper) tin rods are more likely to dissolve copper metal into the tin pool, and severe cases are more likely to cause copper bite/ copper dissolution. It is recommended to regularly check the composition of the tin pool, add new tin rods in time to dilute the copper content, and frequently remove tin slag.
Poor spraying of flux or oxidation of solder feet can also easily cause tin tipping
When the solder leg or the end cut surface of the part is oxidized or the flux spraying is not in place, it may also lead to the occurrence of tin tip. This is because the wettability of the tip of the pin is affected. At the moment when the pin is separated from the tin pool, the tin liquid cannot fully absorb the rebounded tin liquid when it bounces back to the tip of the pin, resulting in the tip of the solder thrown out.
If it is cutting the feet in the factory, it must be noted that the storage time after cutting the feet should not be too long, otherwise the cut surface of the pins will be oxidized, which will cause sharpening problems instead. Check the manufacturer’s incoming materials to confirm that the metal surface has been reworked after cutting the feet deal with.
The problem of self-help flux is that in addition to insufficient spraying, other fluxes such as expired, too thin, and deterioration, will affect the effect of the flux. Of course, if the preheating is too high, the flux will volatilize in advance, and the fluxing effect will be poor, resulting in tin tipping, but these are usually accompanied by other wave soldering problems such as solder empty soldering and pinholes.
